Missing teeth are often the result of trauma (car or sports accidents), tooth decay, poor nutrition or gum disease. While missing teeth may just seem like a cosmetic problem that many people learn to live with, missing teeth are more than just a hole in one’s smile. They can have serious physical and psychological implications that can develop. Missing teeth problems include:
-
Difficulty Chewing – teeth are designed for chewing, so when teeth are missing, it makes it difficult to chew. Chewing can cause pain for the person, causing them to eat less or eat different foods, sometimes resulting in poor nutrition.
-
Shifting Teeth – when there is excess room around a tooth caused by a missing tooth, teeth shift. You may see them gap or crowd each other, causing greater long-term problems, including painful bite misalignment. Tooth decay may become more difficult to reach when teeth begin to collide, which puts them at greater risk to be lost as well
-
Speech issues – which can be embarrassing and diminish self-confidence, just like physical appearance.
-
Bone loss – missing teeth can actually cause bone loss in the jaw and face due to atrophy (the weakening and decrease of tissue) causing a change in your facial structure. In most cases, this leads to looking older and the face shrinking in.
-
Early aging – without your teeth to support the skin around the mouth, the skin can start to sag making those with missing teeth appear older than they are.
-
Compromised mental health – a 2014 study found a link between missing teeth and both depression and anxiety.
-
Loss of confidence – a 2015 study by the American Dental Association found that 23% of people reported embarrassment and avoidance of smiling due to their missing teeth.
-
Missed job opportunities – That same study found 28% of people surveyed felt the appearance of their teeth affected their ability to get a job.
Solutions for Missing Teeth Problems
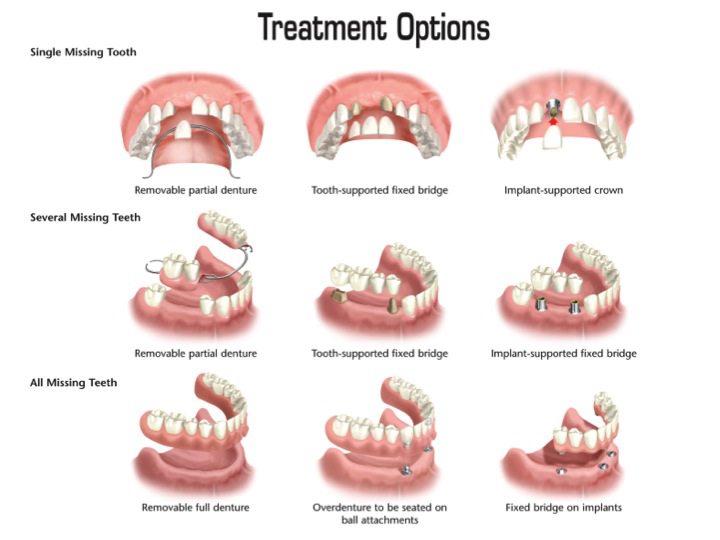
Dental Implants – Dental implants can be used to replace a single tooth or a full set of teeth (and anywhere in between). Secure and stable, they are designed to last for significant time periods and they look, feel and function like real teeth! Dental implants are almost always the best option for replacing missing teeth.
Bridges – Bridges are another possible option when only one or a few teeth are missing. A bridge will be supported by the surrounding teeth, but will eventually need to be replaced.
Dentures – Dentures are often considered a last resort in cases where dental implants are not an option. They are often uncomfortable for the patient and most patients will still experience bone loss/atrophy and the early aging associated with it.
- Tags:
- Metal Braces